
3D DIGITAL GAME ART
The 3D Digital Game Artist draws, models, and animates in different styles depending on the type of game, and is responsible for every aspect, from taking a designer’s brief to using creative, technical, and specialist skills to deliver a marketable game. The challenge is to take a concept and transform it into a 3D mesh which harnesses a wide range of skill sets from good geometry decisions to symmetry and texture.
The artist needs a full understanding of concept art skills and animation as well as the ability to create and animate game characters. The gaming sector continues to experience tremendous growth with the best artists able to lead art teams that push the boundaries on creativity, using the latest technology to design captivating animated experiences.

ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
One of the newest and fastest-growing branches of engineering, Additive Manufacturing is more commonly known as 3D printing.
Traditional manufacturing methods, such as milling and turning, cut away material to create the desired end product. In Additive Manufacturing, layers are added in succession to achieve the same result.
Additive Manufacturing can be a more agile way to create strong and complex objects, such as prototypes, for industry and designers, and with less waste.
Working in Addictive Manufacturing requires a new approach to design and manufacturing. This includes a thorough understanding of the equipment for 3D printing and scanning, and the characteristics of the materials used, along with applied mathematics, geometry, and Computer Aided Design and Engineering (CAD and CAE). An understanding and imagination for the potential future uses of this technology is essential.
One of the newest and fastest-growing branches of engineering, Additive Manufacturing is more commonly known as 3D printing.
Traditional manufacturing methods, such as milling and turning, cut away material to create the desired end product. In Additive Manufacturing, layers are added in succession to achieve the same result.
Additive Manufacturing can be a more agile way to create strong and complex objects, such as prototypes, for industry and designers, and with less waste.
Working in Addictive Manufacturing requires a new approach to design and manufacturing. This includes a thorough understanding of the equipment for 3D printing and scanning, and the characteristics of the materials used, along with applied mathematics, geometry, and Computer Aided Design and Engineering (CAD and CAE). An understanding and imagination for the potential future uses of this technology is essential.

AIRCRAFT MAINTENANCE
A high level of expertise is needed to make sure that aircraft are serviced to rigorous quality and safety standards. An aircraft maintenance technician may specialize in vehicles like helicopters, UAVs (Unmanned Aeronautical Vehicles), or tilt wing aircraft.
The skill calls for technical troubleshooting, repairing, and maintenance of all types of aircraft. As part of a growing and mobile global industry that is increasingly venturing into space, the aircraft maintenance technician will find that the sky is no longer the limit.

ARCHITECTURAL STONEMASONRY
The architectural stonemason works with natural stone, from granite to marble, creating components, and carving and cutting letters on site. A high level of skill and patience is required to create beautiful stonework that will last for generations. Creativity, innovation, accuracy, and problem solving are the hallmarks of a master stonemason.

AUTOBODY REPAIR
When a vehicle has been involved in a collision, it is the job of the autobody repairer to restore it to factory standards and get it back on the road. Every accident is different, so the repairer must be familiar with often-complex mechanical components and how they work.
The autobody repairer needs professional expertise to diagnose the damage to the vehicle and then use a variety of machinery and tools, including welding skills, to make the repair. You need a good knowledge of the range of metals, composites, and plastics used in the manufacture of vehicles in order to restore them to a roadworthy condition.

AUTOMOBILE TECHNOLOGY
Maintaining modern vehicles is a highly skilled occupation that requires a thorough understanding of how they work.
Automobile technicians must be able to work quickly and efficiently without compromising the high standards expected by employers and customers. They must also keep up-to-date with technological advances as modern vehicles get increasingly complex.

BAKERY
Bakers need to demonstrate basic baking skills and an attention to detail to create perfect breads and pastries which are both good to look at, and delicious to eat.
They need an intimate knowledge of the right ingredients of a range of baking products, as well as the optimum temperatures and timings each will require for perfect results.
Bakers also need the ability to work under pressure and to get their products from oven to table within the designated time-frame.

BEAUTY THERAPY
Beauty Therapy work includes a variety of skills from hair-styling, nail and skin care to body massage and make-up expertise.
Beauty therapists work in close contact with their clients and that relationship is at the heart of the job. In addition to demonstrating a wide range of beauty treatment the role also has a therapeutic element which can help the client’s sense of well-being and self-esteem.
The beauty business is subject to changes in styles and trends so it is important to keep in touch with the latest developments in the industry.

BRICKLAYING
Bricklaying is a skill that can be said to be the building block of much of our world. The bricklayer works on everything from our homes to commercial buildings and the walls that surround them.
It is an occupation that requires an ability to follow building design plans precisely through measuring and then constructing in strict accordance with the architect’s plans and local government regulations. It is equally important to execute those plans with high quality professional bricklaying skills.

CABINETMAKING
Craftsmanship is at the heart of cabinetmaking. In an age of mass production, the cabinetmaker produces lasting work designed to be appreciated for many generations. Cabinetmakers must combine creativity and innovation with precision and accuracy and demonstrate a high appreciation of how to use the beauty of wood to best effect.

CAR PAINTING
Restoring a damaged vehicle to its original finish, matching colors, shades, and textures exactly, in a safe and environmentally responsible manner. Vehicles scratched, dented, or damaged in accidents must be returned to the road in showroom condition, with the repaired areas exactly matching the rest of the exterior colour and quality. It could be said that the greatest tribute to a good car painter is when they have finished you cannot see what they have done.
Car painters need to demonstrate great skills in matching paints with the original colour, or on occasion repainting the vehicle in a completely new colour. They must also apply these paints, undercoats and sealants in an environmentally safe and healthy work environment.

CARPENTRY
Carpenters are key members of the construction industry. They are responsible for all the wooden structures involved in building projects, from installing staircases and building roofs to fitting windows and door-frames.
Carpentry is a precision skill which requires accuracy in measuring and cutting so that everything fits into the construction project smoothly and no wood is wasted. Using power and hand tools, a carpenter utilizes ancient and modern techniques to work with wood and to execute perfectly the process of converting raw wood into finished products.

CHEMICAL LABORATORY TECHNOLOGY
Laboratory chemical analysts study substances to determine their chemical composition for research or to develop products. Chemical analysis is necessary to ensure the properties of raw materials, the intermediate stages of the technological processes, and the finished products comply with current standards.
Laboratory chemical analysts use various tools and methods to analyse natural and synthetic materials, as well as performing qualitative and quantitative tests using modern chemical and physico-chemical analytical methods. They need to be well-versed in chemistry and must have adequate knowledge of biology and physics. Critical thinking, time management, decision making, and problem-solving skills are also necessary for this career. Laboratory chemical analysts should be able to act logically and systematically, complying with sanitary and hygienic requirements and occupational safety and health standards.
Laboratory chemical analysts work in the chemical laboratories of quality-control departments, research and development departments, or in environmental departments in plants in chemical, petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries. Greater interest in environmental issues, such as pollution control, clean energy, and sustainability, are expected to increase the demand for chemistry research and development.

CLOUD COMPUTING
Cloud computing specialists help companies migrate their physical information technology activities, such as file storage and on-site servers, into a virtual environment. Cloud engineers typically work at either tech companies or large enterprises with substantial infrastructure.
The skill involves designing and implementing information technology infrastructure in a public cloud environment and features multiple roles including systems engineers, database administrators, network engineers, storage administrators,systems/network/solutions/enterprise architects, programmers / developers, and similar technology-driven roles.
Responsibilities may involve providing design input, collaborating with customer service and analysts on project milestones, and analysing weaknesses and recommending system improvements. Cloud computing specialists need a background working with system architecture components, such as networking and software. In addition to strong technical skills, they should also have excellent collaborative skills, as well as strong analytical reasoning to effectively look at the strengths and weaknesses of projects.
Cloud computing has become a key part of corporate digital transformation strategy. As the cloud begins to dominate the business landscape, demand for positions related to cloud computing is increasing. Those specialists who are adept at managing multi-cloud environments — including public, private and hybrid clouds from a variety of vendors — will be best positioned in the evolving market.

CNC MILLING
Shaping metal and other solid materials using a computer-controlled milling machine to create products used in almost every aspect of modern life, from cars and smart phones to kitchen appliances and prosthetic limbs.
Many of the appliances and objects we use every day depend on Computer Numeric Control (CNC) Milling. It is a highly sophisticated piece of machinery that creates components using precise cutting tools.
The machinist must be able to understand complex technical drawings, and have knowledge and experience of computer skills and software in order to become a skilled machine operator with an understanding of how various metals behave during the cutting process.

CNC TURNING
Creating prototypes from technical designs using a computer controlled lathe that cuts to ultra-fine specifications.
When engineers want to know if a specific part of a design is going to work, they look to CNC Turning. The finished article is used to create pieces of machinery that are often highly-complex. A typical car has around 10,000 parts alone.
A trained operator will be familiar with many types of materials, ensuring the dimensions of the finished piece exactly match the design specifications.

CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION WORK
Concrete Construction workers perform a lot of physical tasks, often beyond the basic responsibility of mixing and delivering the correct amount of concrete to the builders. This includes operating hand and power tools, so learning how to use them safely is vital. Safety is also crucial in preparatory work when erecting scaffolding and carrying out the demolition of old structures.
As with all site workers the concrete construction worker needs to be physically strong and possess manual dexterity. In addition an ability to read and understand blueprints, and to make sure that they match work orders is essential. They also need to work closely with quantity surveyors to make sure there is no wastage of concrete.

CONSTRUCTION METAL WORK
Cutting, assembling, and repairing steel structures ranging from buildings to bridges to construction equipment, using a wide range of metals.
Steel structures are crucial in all areas of construction, from the buildings themselves to the tower cranes needed to assemble them. You will need to understand how the different types of steel need to be used, and how to cut, join, and weld them both in engineering workshops and on site.
For the construction metal worker, that means being able to understand engineering drawings and then building the actual structure accurately.

COOKING
Cooking embraces a wide range of skills from creating menus and preparing dishes for Michelin-starred restaurants, to workplace canteens and cafeterias.
Preparing delicious meals may be the most obvious part of the work of a professional chef, but the job requires much more.
Chefs have to prepare budgets, calculate profit margins, control and order stock, and keep on top of the latest food trends such as organic and vegetarian cuisine and healthy eating regimes.
Communicating well with a team is also part of the high pressure environment in a successful kitchen, while good hygiene is essential for the health and safety of customers and fellow workers.

CYBER SECURITY
Information security analysts work to protect an organization’s computer systems networks, to prevent hackers from accessing and/or stealing sensitive information and data. They are often employed by IT service providers, banking and financial services, government agencies and healthcare companies.
The role typically involves installing firewalls and data encryption software to protect confidential information. Analysts monitor their organization’s network for security breaches and investigate any violations. They may also help design and execute a organization’s disaster recovery plan — the steps and procedures to restore IT systems and networks after an attack.
Information security analysts must stay one step ahead of potential cyber-attackers. They need to keep abreast of attackers latest methods to infiltrate computer systems, as well as new security technologies to counter these threats.
Online business transactions, Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing have grown dramatically in recent years. Coupled with security threats that continue to grow in complexity and frequency, cyber security professionals are in great demand around the world.

DIGITAL CONSTRUCTION
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a way to create and manage information about a project throughout its construction. It provides a complete digital model of the project for all those involved, allowing them to update and improve at key stages.
BIM uses a wide range of software technology through Computer Aided Design (CAD). The process is highly collaborated, allowing everyone from architects and engineers to contractors to work together better, creating buildings with a longer lifespan, and better suited for their purpose.
BIM involves a thorough understanding of the technologies required, including software, cloud computing and IT systems, as well as industry terminology and international standards.
An ability to work collaboratively is essential, along with strong interpersonal skills for working with other project members and clients. Work must meet the highest standards of accuracy and clarity for all potential users.

ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS
Designing and installing electrical systems in all types of commercial, residential, and industrial projects, while carrying out maintenance and repairs safely and quickly.
Electricians are needed wherever there is electricity. They can expect to work in homes, offices, factories, and even farms, carrying out maintenance and repairs, and sometimes designing and installing new systems.
Given the risks associated with electricity, offering a safe and reliable service to customers is paramount. Electricians need to have an intimate knowledge of the latest safety standards and work to a strict code of safety conduct.
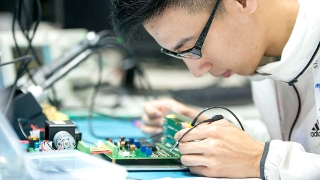
ELECTRONICS
Assembling and wiring products, testing systems, and designing prototype circuits. Variety is the key to a successful career in electronics. Technicians and engineers are needed to operate specialist equipment in workplaces that will range from aerospace and the armed forces to the entertainment industry, robotics, education, health, and telecommunications.
Technicians and engineers will need to understand detailed specifications and international quality standards and keep abreast of the latest developments in technology.

FASHION TECHNOLOGY
Working with fabrics to cut and create clothes for clients from high-end fashion to the latest store designs. A strong sense of fashion trends and appreciation of fabrics are two of the core skills of fashion technology.
Whether designers are creating prototypes for mass production or unique bespoke garments for a single client they will be expected to know how to source, buy, and store raw materials and fabrics and then translate designs into wearable clothes for any occasion.

FLORISTRY
From a small bouquet to a wedding centerpiece, creating a fragrant and beautiful floral display is a talent combining artistry and technical skills.
A successful florist understands the principles of design, aesthetics, composition, and color to capture the mood of the customer.
Florists must also be able to source, purchase, and store floral materials, which by their nature are fragile and short-lived. A florist is aware of which flowers are available in which seasons of the year, and which flowers work well in combination with each other.
Florists are often self-employed or work on commissioned projects, from hotel and retail displays to weddings. They offer advice and translate a client’s vision into displays that are beautiful and captivating.

FREIGHT FORWARDING
Freight Forwarding is a specialist skill organizing shipments of raw supplies or finished goods from the supplier or manufacturer to the point of distribution or final market place.
A forwarder is a master logistician who uses a variety of shipping methods including ships, airplanes, trucks, and rail to ensure that delivery is made in the quickest and cheapest way possible.
Freight forwarders often work internationally organizing the movement of goods between countries. They need to know each country’s export and import regulations as well as the details of waybills, licenses, insurance, and other essential documents.

GRAPHIC DESIGN TECHNOLOGY
Combining the skills of design, art, typography, typesetting, illustration, printing, and publishing to create graphic designs for both online and printed publications.
Graphic Design Technology can employ a variety of specialists within a single team, which might include a graphic designer, graphic artist, prepress operator, typographer, typesetter, type designer, image manipulation specialist, illustrator, art director, production manager, digital printer, information designer, publisher, or packaging specialist.
They work closely with clients from the research and planning stage, through all aspects of the production and printing process, to create a strong visual identity.

HAIRDRESSING
Cutting, styling, treating, and coloring hair for men, women, and children in a work environment that ranges from homes and salons, to film and television productions.
A visit to the hairdresser can be much more than a quick trim. It can involve styling, coloring, and using special treatments. You work closely with your clients and it’s important to have good people and communication skills in addition to a full range of professional hairdressing skills.
The hairdresser is expected to understand different types of hair, to interpret the client’s wishes, and work safely with the products involved.

HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE
Improving the quality of life for clients by working closely with the medical profession to provide care, recuperation, and rehabilitation while promoting physical and psychosocial wellbeing.
A health and social care practitioner delivers health support from initial care to rehabilitation. Through building a close relationship with medical practitioners they are able to support patients and their families to ensure their holistic care needs are met.
Health and social care practitioners will have strong social skills as they work extensively with patients. They will also need a well-developed emotional intelligence to handle some of the more challenging patients and the distress of bereavement.

HEAVY VEHICLE TECHNOLOGY
Repairing and maintaining large stationary and mobile machines and industrial equipment in environments that include transportation, mining, agriculture, and forestry.
Heavy vehicle maintenance technicians must be able to work with internal combustion engines and components. This entails a knowledge of a variety of specific tools such as heavy equipment and power tools to diagnose problems, make adjustments, and repair faults.
Work often has to be done at speed, while observing strict safety standards if vital production time is not to be lost. The technician often works alone and is the link between the employer, the customer, and the manufacturer and can involve a degree of seniority at the highest level of performance.

HOTEL RECEPTION
Hotel receptionists deliver a wide range of guest services: welcome guests to the hotel, make reservations for them and attend to their other needs to keep them happy during their stay. Receptionists work for large hotel chains and smaller, private facilities.
Hotel receptionists work mainly in the hotel’s front office and need to use a wide range of skills, including tourist information, good verbal and written English, computer literacy, good manners, conduct and grooming, excellent communication and social skills, problem solving, competence with figures and cash handling, and the application of procedures for reservations, reception, guest services and check out. Hotel receptionists are vital to every hotel enhancing its reputation and encouraging repeat business.
Globalization, social and demographic changes, and the evolution in transport are driving rapid growth in tourism and travel for business. Business and leisure travel is expected to grow further and demand for hotel receptionists will increase with it.

INDUSTRIAL CONTROL
Installing, troubleshooting, and maintaining industrial automated and electrical production systems.
Automation is of increasing importance in the industrial control of production systems. It requires the ability to troubleshoot, both during installation and in working systems, either across industries or in a specialist area.
Industrial control electricians will need a wide range of skills, learning the installation of cables, instruments and control centers, circuit design and programming. Automation technology is developing rapidly, requiring a strong interest in keeping up with the very latest developments.

INDUSTRIAL DESIGN TECHNOLOGY
Industrial Design Technology combines design and engineering to ensure consumer products work well and look good.
Consumer products for mass consumption need both to work well and look good. This is the role of Industrial Design Technology, which also makes sure that a new product is technically feasible to make, meets the need in the marketplace, and can be sold at an acceptable price.
Industrial Design Technology combines design and engineering. In smaller companies and start-ups, this can mean covering all stages of the process or working as part of a team in larger organizations.
Industrial Design Technology requires a wide range of skills and understanding, including market research, design, engineering, product analysis, materials, and good communication.
You should understand the process of product creation, from concept to production, be good at problem-solving, and be aware of all the tools and techniques to support design and development.

INDUSTRIAL MECHANICS
Industrial mechanics design and plan, install and commission, maintain, repair, and decommission, industrial plant. They work in a large range of industrial settings and production plants and may either have specialist knowledge about one particular industry or work across several. They may be employed within a large single plant, installing and maintaining production equipment, or work for subcontractors across a number of industrial settings. They normally work both indoors and outdoors, on small and large projects.

INDUSTRY 4.0
Industry 4.0 refers to the impact information and communication technologies are having on real-time optimization and networking for efficient automation and production.
It is the role of the Digital Production Systems Technician to implement Industry 4.0 in businesses, designing and implementing systems, introducing both software and hardware, and supporting programs, especially cybersecurity.
A Digital Production Systems Technician must be continually aware of changes and recognize advances in technology means they must be continually learning.
They must understand the business case for implementing Industry 4.0 and design systems accordingly. They should combine strong technical knowledge with an eye on future industry developments, while being constantly aware of risk and security.

INFORMATION NETWORK CABLING
Designing and installing cable systems for telecommunication and network communications.
Essential business services from cable TV to telephones and broadband all depend on Information Network Cabling.
The network cabling technician will use specialist knowledge to design and install Wide Area Networks (WAN), Local Area Networks (LAN), and Cable TV. They will be expected to understand the different types of cables and how they work together to create a successful network.

IT NETWORK SYSTEMS ADMINISTRATION
Providing information technology (IT) services to commercial and public sectors to ensure systems run smoothly and without interruption.
For the IT Network Systems Administrator, the work environment can range from data centers to network operations centers, internet service providers and data centers like climate-controlled server rooms. The ability to communicate, problem solve, and research and understand the latest industry developments is paramount.
Their work involves providing a wide range of services, including user support, design, troubleshooting, and installing, configuring and updating both operating systems and network devices.

IT SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS FOR BUSINESS
Creating new systems and modifying existing ones to provide software solutions to large and small businesses.
One of the areas of greatest demand in today’s business world is providing software solutions.
This can involve creating completely new systems or modifying existing ones, working as part of the team responsible for analysis and design, construction, testing, and maintenance.
This field changes rapidly making it essential to keep on top of the latest developments in the industry to best serve clients.

JEWELRY
Crafting gold and other precious metals and gemstones, using a variety of techniques to create fashion accessories.
The jewelry worker’s job is to take an intricate design, or create one themselves, and turn it into a beautiful piece of jewelry.
They work with detailed designs to create unique pieces of jewelry from precious metals and gems or prototypes using lost-wax casting for mass production. On other occasions they will be asked to duplicate or repair pieces of jewelry.
Understanding and correctly interpreting the designer’s vision is key to jewelry making, along with an appreciation of the precious materials used.

JOINERY
Cutting and joining interior and exterior items, from windows and stairs, to bookshelves and tables, for both commercial and residential projects.
Working from drawings, the joiner’s task is to measure and cut joints then assemble, install, and finish to a high standard.
They are mostly workshop based, but some projects will take place on building sites or in the homes of customers.
Joinery is closely associated with cabinetmaking and carpentry, and other areas of the construction industry.

LANDSCAPE GARDENING
Designing, installing, and maintaining gardens and landscaped areas in private and public spaces.
Landscape gardeners can expect to work on everything from a city park to a country garden, but always with the aim of creating an oasis of beautiful green tranquility.
It means they will be involved in the project from the original concept and design to landscaping, constructing, and planting using a knowledge of soil and weather conditions as well as how plants and trees grow.
They need great creativity and an ability to visualize how designs will look in reality, as well as an appreciation of the impact of a project on the existing natural environment and wildlife.

MANUFACTURING TEAM CHALLENGE
Conceiving, designing, and completing a manufacturing project as part of an effective and efficient team of specialists.
While individual skills are important, being able to work with others as part of a team is the key to the success of any project.
This skill challenge brings together a team of complementary specialists that could include project management, electronics, programming, machining, and computer aided design. Time, cost, and quality are all factors in this competition.
It means that in addition to individual talents, participants must contribute to the team as a whole, showing self-awareness, interpersonal skills, and thinking outside the boundaries of their own area of expertise.

MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAD
Using computer software as a tool to create and improve manufacturing projects from ship-building to the aerospace industry.
Computer aided design (CAD) uses specialist software to create two and three dimensional images and animations of projects both in manufacturing and for use in advertising and technical manuals.
CAD can convey many types of information, including dimensions, types of material, and tolerances and is essential in offering solutions to both engineering and manufacturing problems.
By producing photorealistic animations and videos, it can simulate how a design will actually function in the real world.

MECHATRONICS
Building automated systems for industry using mechanics, electronics, pneumatics, and computer technology.
Mechatronics includes mechanics, pneumatics, electronically controlled systems, programming, and robotics and systems development.
It is the job of the mechatronics technician to combine these areas to design, build, maintain, and repair automated equipment, and programme equipment control systems.
As well as factory assembly lines, mechatronics is used in everything from bottling machines to supermarket cash till and belt assemblies.

MOBILE APPLICATIONS DEVELOPMENT
Mobile Applications Developers use technology and design to create apps which are appealing and function well on phones.
We use apps on our phones every day. It is the job of Mobile Applications Development to create these essential tools for almost every aspect of our lives.
As a rapidly increasing way of communicating and sharing information, this is one of the fastest growing occupations, offering opportunities for both employment and self-employment, especially for young people.
As such, you may have a tightly developed role for a company in a specific sector, such as delivery or sales, or be able to offer tailored solutions to smaller businesses as a freelancer.
Mobile Applications Development requires an understanding of technology and design to make an app that is appealing and functions well. You must understand the client’s requirements and create a test-driven framework for a product that is reliable, updatable, and that the user can understand and use with ease.

MOBILE ROBOTICS
Designing, building, and maintaining robots to solve problems in industries from manufacturing to aerospace, mining to medicine.
Robots play an increasing role in our lives and places of work in areas as diverse as manufacturing, agriculture, aerospace, mining, and medicine.
Mobile robots begin with a design and then a prototype which must be programmed and tested to make sure it offers a high and consistent level of performance.
The mobile robotics engineer must be familiar with logic, microprocessors, and computer programming and prepare specifications for the robot’s capabilities as they relate to the work environment. They are also responsible for cost efficient design, cost-price calculations, and quality control.

OPTOELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY
Optoelectronics is an emerging technology used in a range of applications from lighting products to medical research and treatment, advanced manufacturing devices to measuring technology.
Optoelectronics combines the physics of light with electricity so that one can control the other. We see it in products like LED lights, solar cells, and optical fibre cables, among many.
Its applications are equally wide, from lighting products to medical research and treatment, advanced manufacturing devices and measuring technology.
Optoelectronic Technicians can also work in a diverse range of fields, including development, production, and maintenance. They must work with accuracy and precision and meet customer specifications and international standards. They can be involved in manufacturing, commissioning, and providing support for these devices.
Optoelectronic Technicians must be able to work with optical, electrical, magnetic, and mechanical systems in the manufacture of devices. They must be familiar with the environmental impact on systems when installing them and be up to date with the changes brought by new technologies in the industry. It is a fast-growing occupation with prospects to develop both a broad and specific range of expertise.

PAINTING AND DECORATING
Using paint, decorative coatings, wallpaper, gilding, and sign writing both indoors and outdoors in a wide variety of working environments.
The services of the painter and decorator are needed everywhere from homes to public buildings, factories, and offices.
Painters and decorators can expect to offer professional advice on colours and designs and employ a wide range of finishing skills.
Painting and decorating is a creative job that requires a sense of design as well as the core skills of painting, decorative coatings, and gilding.

PATISSERIE AND CONFECTIONERY
Creating hot and cold sweet treats using edible materials that are a delight both for the eye and the taste buds.
Confectionery can range from petit fours to chocolates and candies. They can be served hot or cold everywhere from hotels and restaurants to specialist stores.
Confectioners will need to be skilled in designing great products using sugar, icing, chocolate, and other sugar-based ingredients. It is a job for an artistic creative mind but one which requires solid catering and cooking skills if those creative ideas are to become a delicious reality.
Many years of training go into making the best confectioner and pastry cooks, who also show flair and creativity, working with many different materials and types of equipment.

PLASTERING AND DRY WALL SYSTEMS
Plastering flat surfaces, installing drywall systems, and creating decorative moldings on projects from private homes to historic houses.
Plasterers work on both inside and outside surfaces, often creating metal frames and installing plasterboard to create drywalls before applying the final plaster surface.
They will know how to interpret plans using a range of materials and are able to work on projects that include curved surfaces, windows, doors and decorative molding.
Plasterers are typically employed as sub-contractors for work on domestic and commercial projects, as well as heritage sites.

PLASTIC DIE ENGINEERING
Designing and creating plastic molds from designer drawings for mass produced products of high quality and low cost.
Plastic die engineers are a crucial link in the manufacturing chain of products that range from cars, phones, home appliances, medical equipment, and anything that requires plastic.
They will create moulds using CAD/CAM computer assisted machining systems to be installed in injection moulding machines for the manufacture of plastic products.
A plastic die engineer needs high levels of skill in numeracy, hand and machining skills, polishing, assembling, testing, and troubleshooting.

PLUMBING AND HEATING
Installing plumbing and heating systems in a diverse range of projects associated with the construction industry.
We all depend on plumbing and heating technicians for hot and cold fresh running water in our homes and offices and for staying warm in cold weather.
Plumbing and heating technicians need to be able to plan and design systems, then install and test them. On occasion they will also need to diagnose faults and make repairs.
The plumbing and heating technician works both indoors and outdoors, in homes, and in commercial projects as a key part of the construction industry.

POLYMECHANICS AND AUTOMATION
Producing and installing parts for production machinery and equipment in areas that include electrical and mechanical engineering, and fitting hydraulics and mechanics.
Polymechanics technicians need a wide range of skills, both producing and installing parts for production machinery and equipment.
They require skills in logic and automation control and the related basic electrical and circuitry work associated with these areas of production.
They need to diagnose and solve problems and offer advice on a wide range of issues in many different industries.

PRINT MEDIA TECHNOLOGY
Keeping the presses rolling for all kinds of printed materials that are needed by a wide range of customers.
The print media technology professional is responsible for all aspects in the production of printed materials, most often using traditional ink on paper, but also newer digital technologies like toner on paper.
This begins with planning and preparation, running the machines efficiently and effectively to ensure high quality, and cleaning up once the run is complete.
They need to understand the complex machinery involved, know the different types of paper, operate cutting equipment, and even be able to mix custom inks at the customer’s request.

PROTOTYPE MODELLING
Creating prototypes that allow engineers and designers to test, assess, and modify during the process of product development.
Prototypes are essential if designers are to understand how a product will perform. They allow testing of function and performance in the real world, and even determine if customers want to buy them.
The prototype modeller must also have a wide range of skills, including 3D CAD systems, CAM systems such as milling, printing, vacuum casting, working with machine and hand tools, as well as spray painting and finishing.
Often multiple versions of a prototype must be created, each designed to test what is still uncertain in the performance of the final design.

RAIL VEHICLE TECHNOLOGY
Rail Vehicle Technician carry out inspections, maintenance and repair, and general troubleshooting on rail vehicles.
Railways are as important today as when they first began nearly 200 years ago, transporting large numbers of people and goods quickly and in a way that is friendly to the environment.
Today’s rail vehicles, though, are more complex than ever. It is the job of the Rail Vehicle Technician to carry out inspections, maintenance and repair, and general troubleshooting.
To ensure safe and reliable trains, they must work in a team with an understanding of a wide range of technologies, including high voltage electricity, brakes, air conditioning, door operations, and wheels.
Rail vehicle technicians have the ability to work as a team while using their individual specialist knowledge to enhance its performance. They must continuously improve their diagnostic skills to keep up with technology, work to deadlines and plan maintenance schedules. This is a global industry that offers the prospect of advancement to technical and managerial positions.

REFRIGERATION AND AIRCONDITIONING
Keeping refrigeration and air conditioning working is essential to the modern world. The refrigeration and air conditioning engineer is responsible for the design, installation, maintenance, and repair of both systems.
Their work involves domestic and commercial settings, as well as including the construction and transportation sectors, for example in ships and trucks.
Finding solutions to issues involving climate and the environment are the biggest issues for engineers in the refrigeration and air conditioning industry.

RENEWABLE ENERGY
Renewable Energy Technicians ensure the equipment for collecting, generating, or distributing power from a wide variety of sources including wind, water, solar and geothermal, is properly maintained and operates efficiently.
Renewable Energy is central to solving our current climate crisis and ensuring the health and growth of future economies.
It uses a wide range of sources to supply power, from wind and water to solar power, organic matter, and even geothermal heat from the earth’s core.
It is the role of a Renewable Energy Technician to ensure the equipment for collecting, generating, or distributing power from their sources is properly maintained and operates efficiently.
A Renewable Energy Technician can expect to work both indoors and outdoors and in conditions that are often challenging, including extremes of heat and cold, at heights, and in remote locations.
Problem-solving skills are essential, along with a detailed knowledge of the different technologies and the tools needed to work on them. Physical strength is needed to lift heavy equipment and operate power tools while following health and safety rules.

RESTAURANT SERVICE
Providing food and drink services to guests in hotels and restaurants, showing attentiveness, and understanding of their needs and expectations.
For a memorable meal the quality of the service is something that guests often remember as much as the food and drink served.
That means that restaurant servers must show extensive knowledge of all types of cuisine and dishes, especially the ingredients and cooking style of the dishes on an a la carte menu. They will need to know and understand the methods of preparation and serving, along with the tools used.
Regardless of whether it is a self-service cafeteria or a five star hotel restaurant good manners, a smart appearance, and impeccable personal hygiene are equally essential.

ROBOT SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
Robot Systems Integration ensures that robots fit properly in the production process. The number of robots used in industry has increased rapidly, with an estimated 400,000 installed every year. Robot Systems Integration ensures that they fit properly in the production process.
In order to perform complex and precise tasks, robots rely on skilled human resources to install and maintain them.
Robot integrators must be able to assess the best type of robot for a particular task, which might include lifting, loading and unloading, and welding, and then deciding where to place them.
Other considerations include managing the flow of parts, developing and installing suitable programming, and the safety of the human workforce around them,
A Robot Systems Integration technician will provide technical solutions for incorporating them into production processes, from the preliminary assessment to connecting them to power and to other automated systems.
They should be aware of the latest developments in manufacturing and control systems, including the multi-articulated arm, and the evolution of regulations for robotization.
While larger businesses such as motor manufacturing were early adopters of robots, their potential for small and medium-sized business (SMEs) represents a large and growing opportunity for skilled technicians.

VISUAL MERCHANDISING
Creating eye-catching visual displays for the windows and interiors of shops and department stores, designed to maximize sales.
Having good products is only part of the key to a successful retail outlet. Drawing people in by using visual appeal is also important.
The visual merchandiser creates a positive atmosphere for customers, creating a brand look that is creative, eye catching, and drives sales.
They need to understand the target market for both products and outlets, have a good sense of design to implement a brief, and show careful attention to detail.

WALL AND FLOOR TILING
Laying tiles accurately and a high level of finish in a variety of materials in residential, commercial, and public projects.
Tiles can be made of ceramics, mosaic, and natural stone. Likewise the environment in which they are used is equally diverse: walls, floors, and staircases in houses, offices, gardens, factories, public buildings, and places of worship.
That means that they may be expected to work both inside and out, accurately following designs, preparing surfaces, and laying tiles to the correct pattern and grouting to a high standard.
Tilers sometimes specialize in certain areas of artistic work, for example the complex designs seen in swimming pools.

WATER TECHNOLOGY
Inspect water samples, supervise filter systems, process pipes out of metal or plastic and maintain and repair pipes or small electric devices.
Water supply engineering technicians ensure that enough drinkable water is available every day. Drinkable water is our most precious food, which needs special protection. Before water can get processed to become drinkable water, it needs to be extracted. From wells or springs, for example. After its treatment in filter systems, it gets stored and distributed. These are all steps, which water supply engineering technicians take care of.
They inspect water samples, supervise filter systems, process pipes out of metal or plastic and maintain and repair pipes or small electric devices. They work at waterworks or pipe networks and complete their tasks oftentimes in teams under the management of a master craftsman or foreman.

WEB TECHNOLOGIES
Planning and designing, as well as testing websites, maintaining them, incorporating third party platforms, and integrating social media platforms.
Working with web technologies is a key skill in a world that increasingly places the web at the heart of a modern platform. It is also one of the most complex and diverse of all skills.
Web designers and developers will first establish a professional relationship with clients to develop a deep understanding of the requirements for their website. Strong design and communication skills, coupled with a grasp of target audiences, markets, and trends are all essential. During the development process, web designers and developers create databases, build programmes, as well as test and debug websites.

WELDING
Preparing and joining various types of metal using both electrical, and electric/gas processes. Welders work with different metals to cut and join everything from steel beams to pipes, plates, and pressurized vessels.
Being able to operate the various types of welding equipment both safely and accurately is of the highest importance. This can include the latest types of submerged arc, plasma arc, stud welding, and laser welding.
Welders need to prepare and finish joints in a wide ranges of industries and locations, from a factory workbench or construction site to a power station or ship at sea.
